Treemap
Where possible, use qlik-embed and qlik/api rather than this framework.
Treemaps display hierarchical data by using nested rectangles, that is, smaller rectangles within a larger rectangle. Use a treemap when space is constrained and you have a large amount of hierarchical data that you need to get an overview of. Treemaps should primarily be used with values that can be aggregated.
Learn more about the treemap chart, or review the treemap chart API specification.
In the example below, you have several product groups, such as Produce, Canned Products, and Frozen Foods. Each product group consists of a large rectangle. You can regard the product groups as branches of the tree. When you select a product group, you drill down to the next level, the product type, for example, Vegetables, Meat, and Dairy. You can regard the product types as sub-branches of the tree. This is a treemap created with two dimensions.
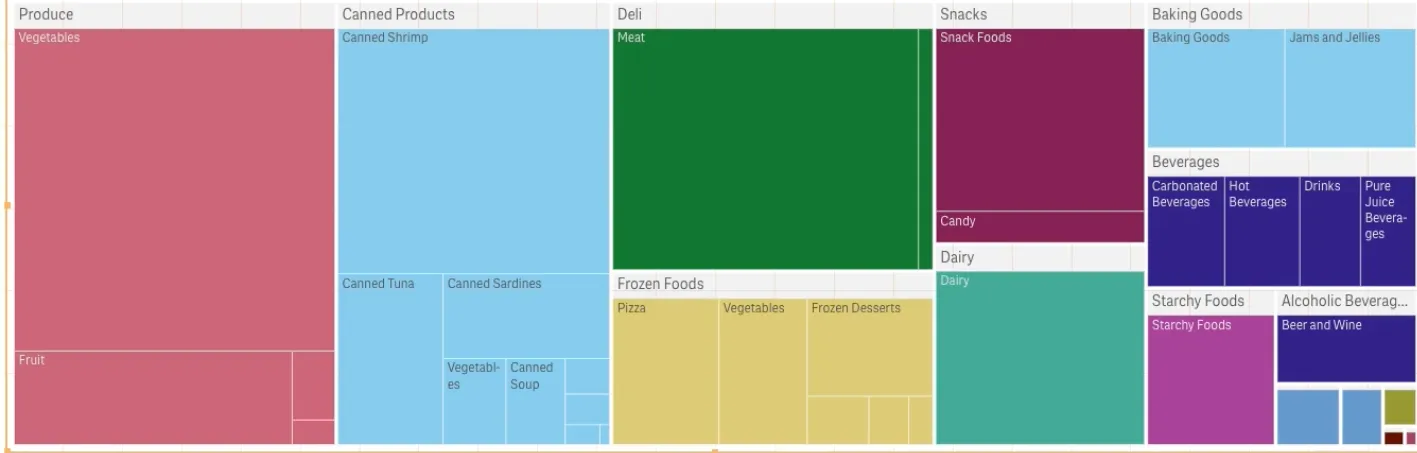
// Configure nucleusconst nuked = window.stardust.embed(app, { context: { theme: "light" }, types: [ { name: "treemap", load: () => Promise.resolve(window["sn-treemap"]), }, ],});
// Rendering a simple combo chartnuked.render({ element: document.querySelector('[data-key="treemap"]'), type: "sn-treemap", fields: ["Product Group", "Product Type" "=Sum(Sales)"],});In a treemap, you need at least one dimension and one measure, but to make full use of the treemap it is preferable to have two or three dimensions. You can only have one measure, but up to 15 dimensions. It is not recommended using more than three dimensions as the treemap may become unmanageable.
Requirements
Requires @nebula.js/stardust version 1.2.0 or later.
Installing
If you use npm: npm install @nebula.js/sn-treemap.
You can also load through the script tag directly from
https://unpkg.com.
More examples
Treemap with three dimensions and one measure
The treemap below is created with three dimensions and a measure. Here you have several product groups divided by region where each region consists of a large rectangle. You can regard the regions as branches of the tree. When you select a region, you drill down to the next level, the product group. You can regard the product groups as sub-branches of the tree and those branches have their own leaves. A leaf node’s rectangle has an area proportional to a specified dimension of the data. Sorting is automatic according to the size.
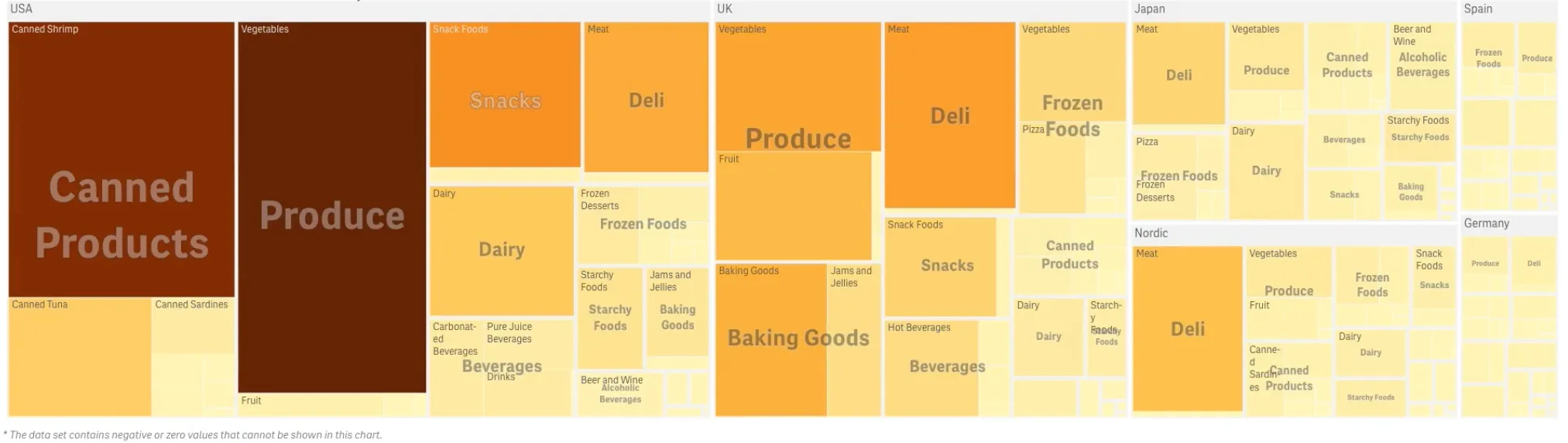
nuked.render({ element: document.querySelector('[data-key="treemap"]'), type: "sn-treemap", fields: ["Region", "Product Group", "Product Type" "=Sum(Sales)"],});When you have created the treemap, you may want to adjust its appearance and other settings in the properties panel.
If the data set contains negative values, a text message is shown stating that the negative values cannot be displayed.
Use color by measure or dimension
When there is a correlation between color and size in the tree structure, you are able to see patterns that would be difficult to spot in other ways, for example, when a certain color is particularly relevant. By default, the coloring is by dimension, with 12 colors, but that can be changed in the properties panel. When you have more than one dimension, you can decide which dimension to color by. The first example below shows - color by dimension.
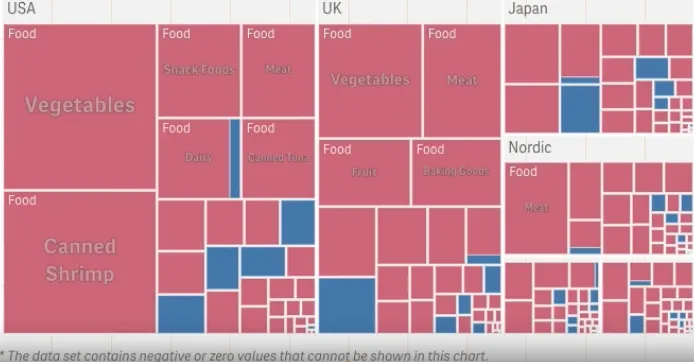
nuked.render({ element: document.querySelector('[data-key="treemap"]'), type: "sn-treemap", fields: ["Region", "Product Type", "Product Line" "=Sum(Sales)"], properties: { color: { mode: "byDimension", byDimension: {label: "Product Line", type: "expression"}, }, },});In the example below, the coloring is by expression (Avg(Margin)), a calculated measure, and by using this expression, you can see which items have the highest average margin. The darker the color, the higher the average margin.
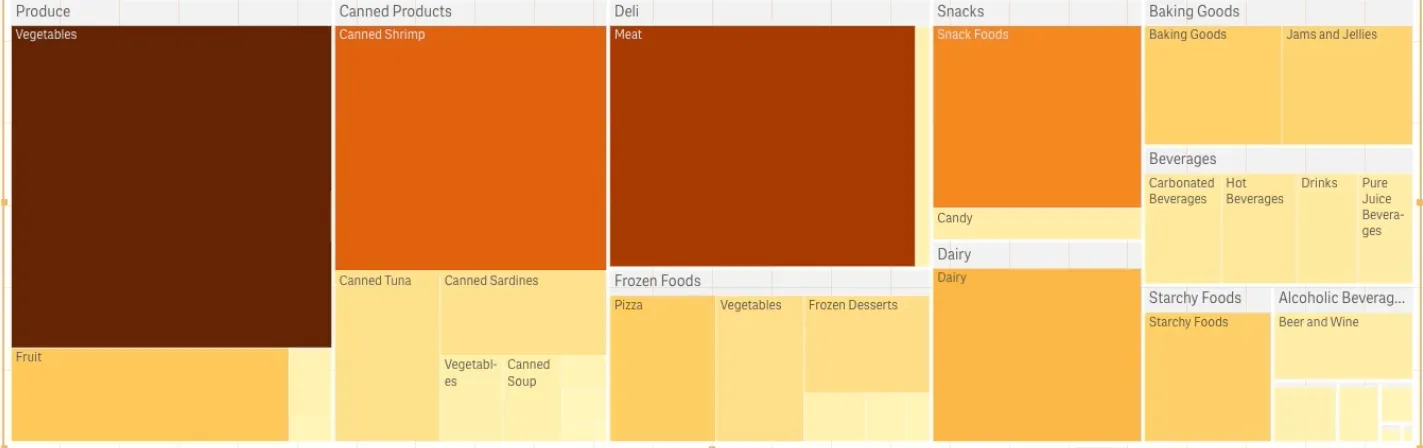
nuked.render({ element: document.querySelector('[data-key="treemap"]'), type: "sn-treemap", fields: ["Product Group", "Product Type" "=Avg(Margin)"], properties: { color: { mode: "byMeasure", byMeasureDef: {label: "Avg(Margin)", type: "expression"}, }, },});