Content Security Policy
Overview
This tutorial explains the concept of content security policy (CSP) and shows how to modify CSP policies in your Qlik Cloud tenant.
CSP is a methodology implemented in modern web browsers to disallow a webpage from accessing resources outside its own origin without explicit permission. The intent is to prevent or mitigate cross-site scripting and data injection attacks when a user navigates to a web application.
You can find an in-depth explanation of content security policy on the Mozilla website.
Content Security Policy and Qlik Cloud
There are two main cases where content security policy is necessary to support user experiences with cross-site implications:
- Using visualization extensions in Qlik Sense applications
- Embedding iframe content via the app or single integration APIs into external web applications
Using visualization extensions in Qlik Sense applications
If you have uploaded extensions into your tenant, chances are they
contain references to code, CSS style sheets, or images hosted on a website
outside of the qlikcloud.com domain. In order for these extensions to function
properly in the Qlik Sense user experience, content security policy needs to be
configured to allow the content from the hosting domain. There are several
directives you can set to permit the content to be accepted by the
browser.
You can find a list of directives you can set in a content security policy entry on Qlik Help.
Embedding iframe content into external web applications
When you embed iframe content using the app integration or single integration APIs like visualizations, sheets, or entire analytics experiences into your web applications, adding a content security policy reference is necessary to allow the content to render in the application.
This does not apply when using the qlik-embed framework.
When content security policy blocks content in the browser
If you embed content from your tenant or use visualization extensions and they aren’t rendering in the browser, content security is most likely blocking it. Opening your browser’s developer tools console will show an error describing the missing directives resulting in the block.
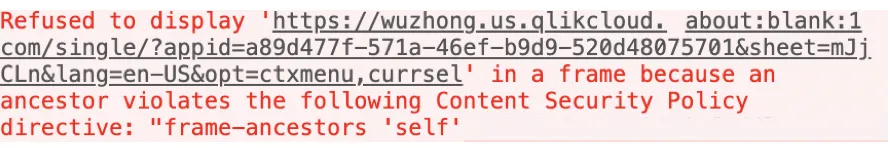
In this example, the browser is blocking an iframe embedded into a web page. The
error states the frame-ancestors directive is not set for the website
attempting to render the content.
Configuring content security policy
To set up a content security policy directive, access the management console for your tenant.
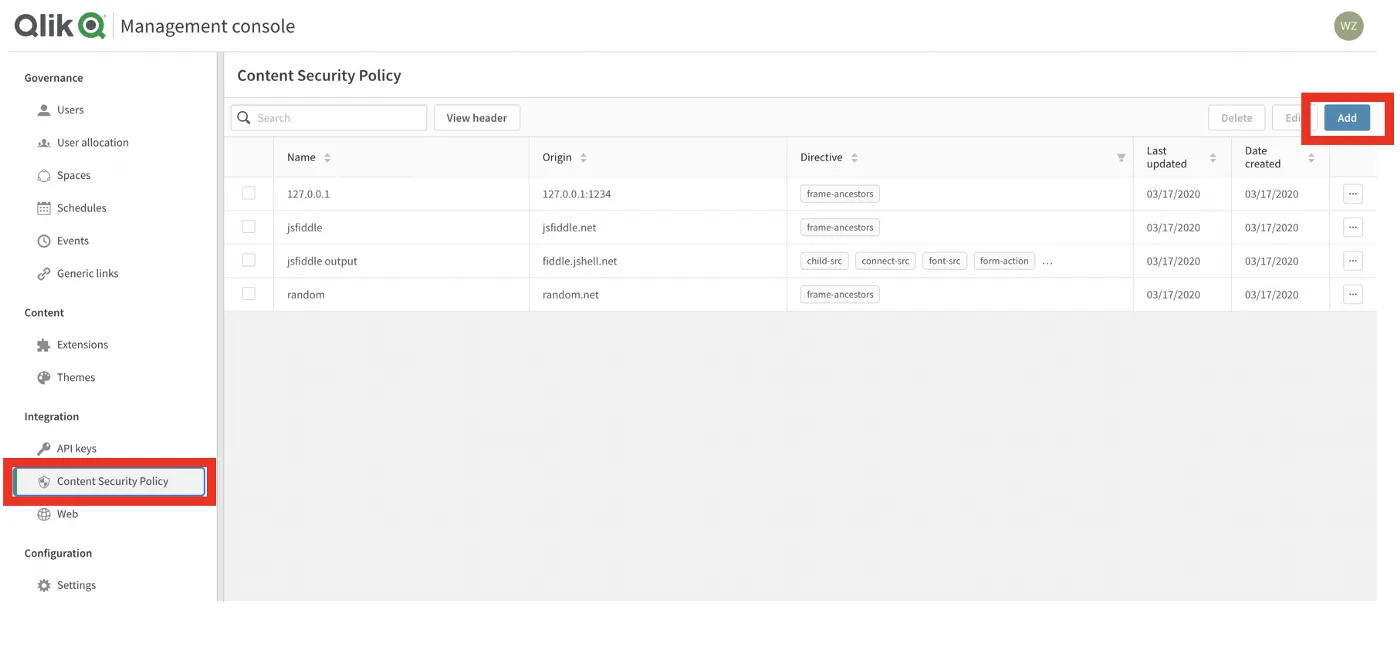
In the left pane, select “Content security policy”. Click “Add” on the top right.
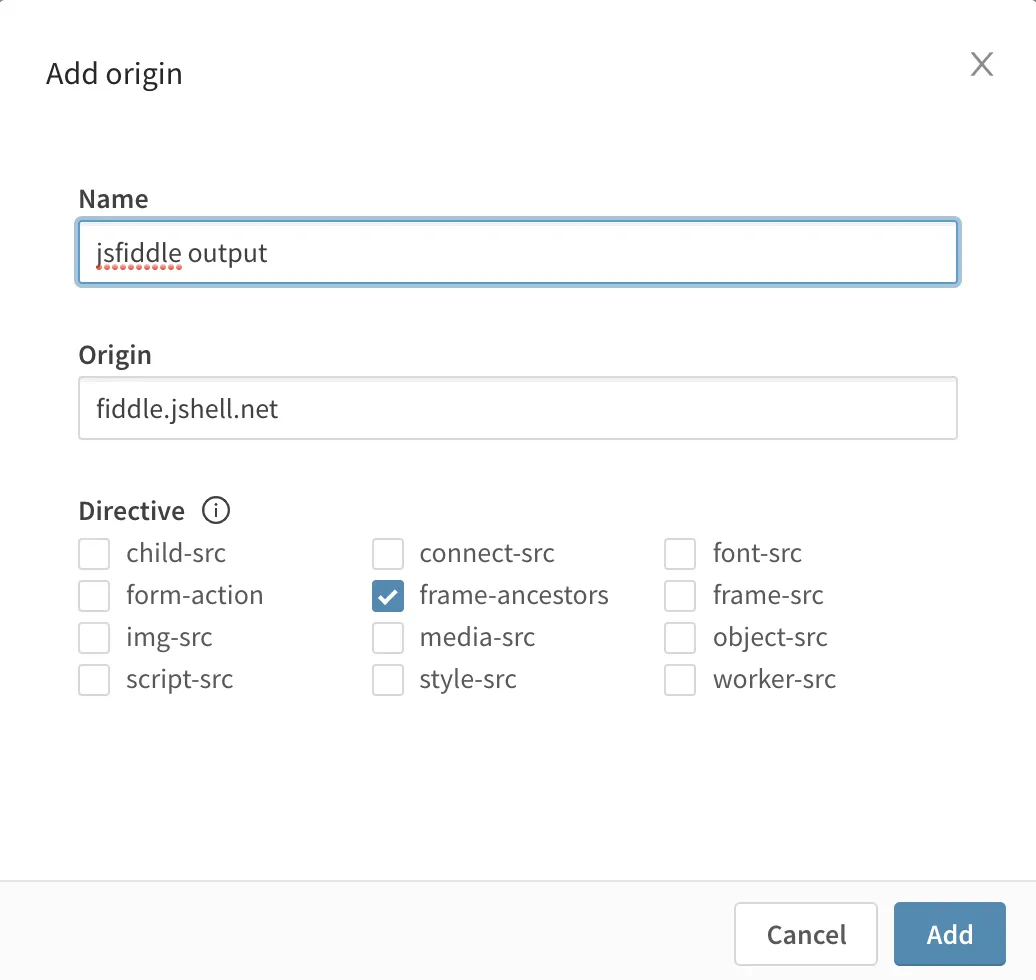
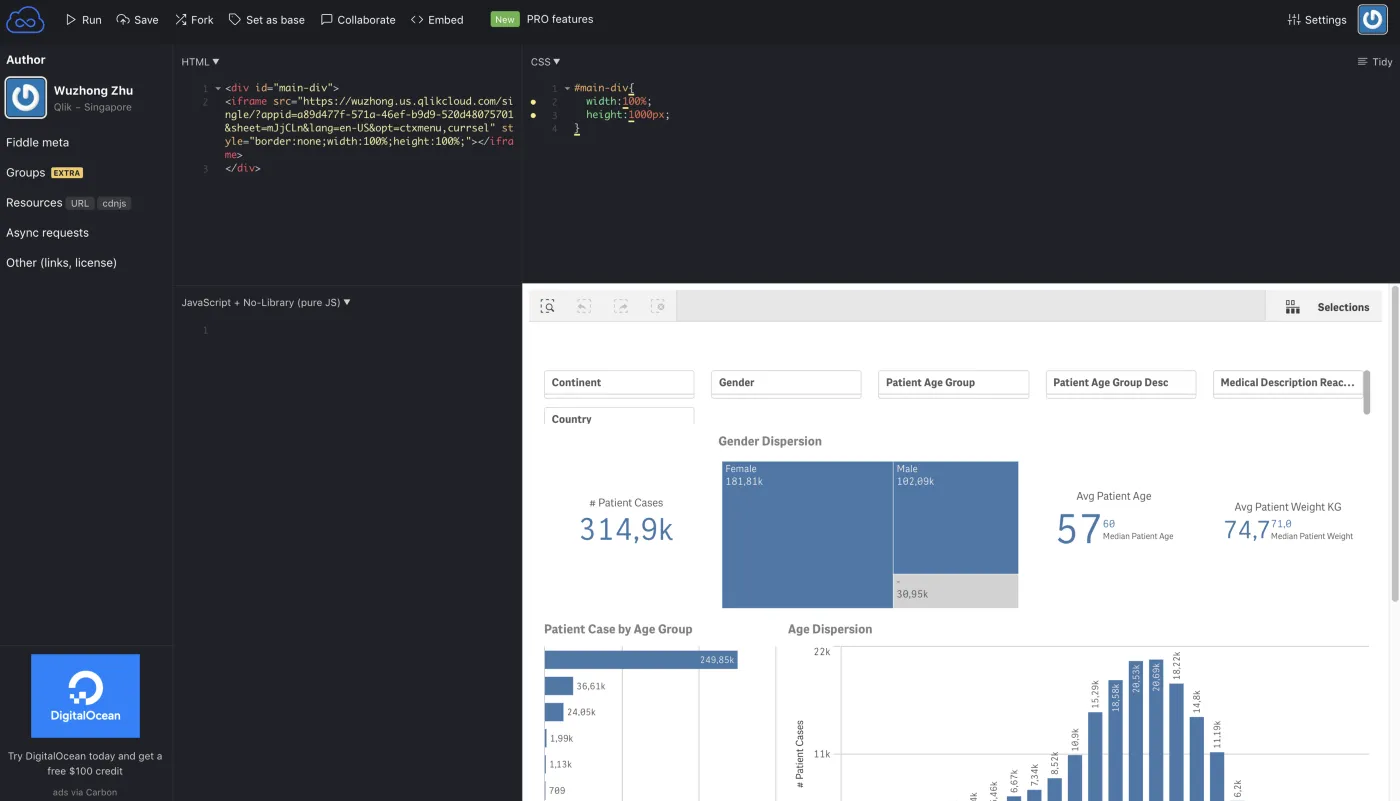
The example embeds a sheet from a Qlik Sense application using iframes via the single
integration API into a
jsfiddle code sample. The origin is set to the domain for jsfiddle
fiddle.jshell.net and the directive frame-ancestors is checked to allow the
sheet to render in the jsfiddle web page.
Summary
Now that you know what content security policy means and how it works, you can establish the appropriate access on Qlik Cloud to allow content to work seamlessly for embedded experiences and integrated components.